lv dysfunction grades | left ventricular dysfunction stages lv dysfunction grades To provide for tissue perfusion without pulmonary congestion, the left ventricle (LV) must eject an adequate stroke volume at arterial pressure (systolic function) and fill without . Alexandre Maltas Law Corporation. Office. Vancouver. Phone 604 891 7235. Fax 604 682 5217.
[email protected]. vCard. Legal Administrative Assistant Courtney Litvinsky 604 443 .
0 · symptoms of left ventricular dysfunction
1 · side effects of left ventricular dysfunction
2 · left ventricular dysfunction tee
3 · left ventricular dysfunction stages
4 · left ventricular dysfunction normal range
5 · left ventricular dysfunction mild
6 · left ventricular dysfunction
Rich in local history, the Aldie Mill Historic Park offers patrons a chance to step into the early 1800s and experience a taste of industrial life and culture from days of yore. Constructed.
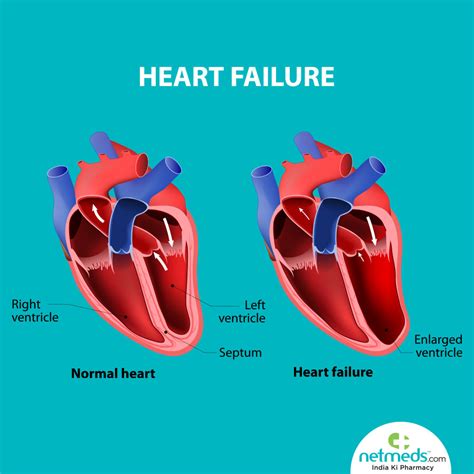
To provide for tissue perfusion without pulmonary congestion, the left ventricle (LV) must eject an adequate stroke volume at arterial pressure (systolic function) and fill without .This document provides recommendations for the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography, including Doppler and 2D imaging variables. It also discusses the diagnosis .This document summarizes the 2016 ASE recommendations for evaluating left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography. It includes parameters, algorithms, and flow charts for .
sac air dior
Diastolic dysfunction is a condition that causes heart failure with normal systolic function. It is often caused by hypertension or ischemia and can be diagnosed by echocardiography. Learn.What are the grades of diastolic dysfunction? Healthcare providers use a grading system to determine how severe diastolic dysfunction is: Grade I is slightly impaired diastole. It is a . This article reviews the echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular diastolic function and its association with cardiovascular events. It also discusses the challenges and options for indeterminate diastolic function and .Learn how to grade diastolic dysfunction and estimate LV filling pressures using echocardiography. Download the updated recommendations, webinars, posters, and pocket guides from the American Society of Echocardiography and the .
Grading of DD is classically as follows: grade I, impaired relaxation and decreased suction of the LV; grade II, pseudonormalization, increased stiffness of the LV, and possible elevated filling pressure; and grade III, .
In the present review, we aim at rationalizing the applicability of the recent recommendations to the perioperative and ICU areas, discussing the clinical meaning and . LVDD is a condition that affects your heart’s ability to fill up with blood before sending it out. It can be caused by aging, heart problems, or COVID-19 and can lead to heart failure. Learn about. To provide for tissue perfusion without pulmonary congestion, the left ventricle (LV) must eject an adequate stroke volume at arterial pressure (systolic function) and fill without requiring an abnormally increased left atrial pressure (diastolic function).
This document provides recommendations for the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography, including Doppler and 2D imaging variables. It also discusses the diagnosis and prognosis of diastolic dysfunction and heart failure in different clinical settings.This document summarizes the 2016 ASE recommendations for evaluating left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography. It includes parameters, algorithms, and flow charts for diagnosing diastolic dysfunction and estimating LV filling pressures. Diastolic dysfunction is a condition that causes heart failure with normal systolic function. It is often caused by hypertension or ischemia and can be diagnosed by echocardiography. Learn.What are the grades of diastolic dysfunction? Healthcare providers use a grading system to determine how severe diastolic dysfunction is: Grade I is slightly impaired diastole. It is a common finding in people over age 60. Grade II is elevated pressure in the left side of your heart.
This article reviews the echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular diastolic function and its association with cardiovascular events. It also discusses the challenges and options for indeterminate diastolic function and the cutoff values of E/e' ratio in normal subjects.
Learn how to grade diastolic dysfunction and estimate LV filling pressures using echocardiography. Download the updated recommendations, webinars, posters, and pocket guides from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Grading of DD is classically as follows: grade I, impaired relaxation and decreased suction of the LV; grade II, pseudonormalization, increased stiffness of the LV, and possible elevated filling pressure; and grade III, restrictive filling with elevated filling pressure and noncompliant LV. In the present review, we aim at rationalizing the applicability of the recent recommendations to the perioperative and ICU areas, discussing the clinical meaning and echocardiographic findings of different grades of LVDD, describing the impact of LVDD on patients’ outcomes and providing some hints on the management of patients with LVDD.
LVDD is a condition that affects your heart’s ability to fill up with blood before sending it out. It can be caused by aging, heart problems, or COVID-19 and can lead to heart failure. Learn about.
To provide for tissue perfusion without pulmonary congestion, the left ventricle (LV) must eject an adequate stroke volume at arterial pressure (systolic function) and fill without requiring an abnormally increased left atrial pressure (diastolic function).This document provides recommendations for the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography, including Doppler and 2D imaging variables. It also discusses the diagnosis and prognosis of diastolic dysfunction and heart failure in different clinical settings.
This document summarizes the 2016 ASE recommendations for evaluating left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography. It includes parameters, algorithms, and flow charts for diagnosing diastolic dysfunction and estimating LV filling pressures. Diastolic dysfunction is a condition that causes heart failure with normal systolic function. It is often caused by hypertension or ischemia and can be diagnosed by echocardiography. Learn.What are the grades of diastolic dysfunction? Healthcare providers use a grading system to determine how severe diastolic dysfunction is: Grade I is slightly impaired diastole. It is a common finding in people over age 60. Grade II is elevated pressure in the left side of your heart. This article reviews the echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular diastolic function and its association with cardiovascular events. It also discusses the challenges and options for indeterminate diastolic function and the cutoff values of E/e' ratio in normal subjects.
Learn how to grade diastolic dysfunction and estimate LV filling pressures using echocardiography. Download the updated recommendations, webinars, posters, and pocket guides from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Grading of DD is classically as follows: grade I, impaired relaxation and decreased suction of the LV; grade II, pseudonormalization, increased stiffness of the LV, and possible elevated filling pressure; and grade III, restrictive filling with elevated filling pressure and noncompliant LV.
sac saddle dior beige
symptoms of left ventricular dysfunction
rouge dior in 772 matte
side effects of left ventricular dysfunction
left ventricular dysfunction tee
157. Carbohydrates. 11.8g. Fat. 0g. Protein. 1.2g. ABV. 5.8% Ingredients List: Water, Barley Malt, Corn Syrup* (Dextrose, Maltose), Yeast, Hop Extract. Corn Syrup Disclaimer: *Corn syrup is used as a part of the .
lv dysfunction grades|left ventricular dysfunction stages